The term AGV refers to robots that replace humans in the work of transporting goods. Automated Guided Vehicle, as its name, this is a type of robot that has wheels and can automatically move, carry and pull goods. In recent years, in efforts to reduce labor and increasing demand for freight, AGV has received more and more attention. Indeed, nowadays it has become a rapidly growing field. and is widely applied in factories and warehouses.
On the contrary, although collectively called AGV, the function and shape are increasingly developed, there are many different types and designs, making many people wonder “Don’t know which type to choose”
Therefore, in this article, we will introduce in detail some important things before putting the AGV into practical use, such as “which type to choose, how to choose the type with guiding method”.
Contents
What are AGV and AMR?
AGV stands for Automated Guided Vehicle, a word that indicates a robot that replaces the work of transporting goods which was previously performed by humans.
As the name suggests, the AGV is a wheeled robot that can automatically transport, load, and pull goods. Depending on the size of the goods, the size of the AGV also varies, from compact AGVs that can transport small products to large AGVs that can carry containers.

AMR stands for Autonomous Mobile Robot – “Intelligent self-propelled robot”, a word that indicates a robot that can both move and transport automatically in the factory.
Unlike AGV, AMR does not need to use accompanying devices such as magnetic lines. It can automatically move, transport without having to change much in layout, floor and cart in the factory.
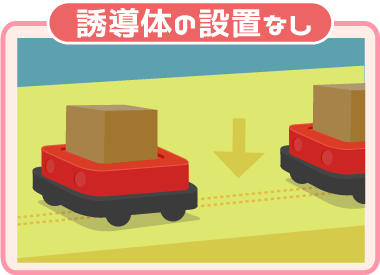
AGV’s mode of transport
Before putting the AGV into practice, it is necessary to select the type of AGV with the appropriate features for the factory. It is important that we want to transport “What” and “How”.
In this article, I will introduce the loading method of each type of AGV.
1. Loading type
As for the loading type, it is built to resemble a trolley with handles, which is an AGV vehicle that can directly load onto the vehicle and transport. The repetitive transportation jobs that humans often do will be replaced by AGV self-propelled vehicles, thereby reducing heavy work and preventing risks for workers.


2. Pulling type
The pulling AGV is a vehicle that does not directly place the goods on it, but towing them, pulling the goods one after another at the back. It is possible to pull a lot of goods carriages in a row at the back like a train, if in case you want to ensure the width of the path, you can try to transport many goods in a few times.
It is possible to choose an AGV suitable for the weight of the goods to be transported, from the AGV towing several tens of kilograms to the towing AGV truck that can tow several tons.

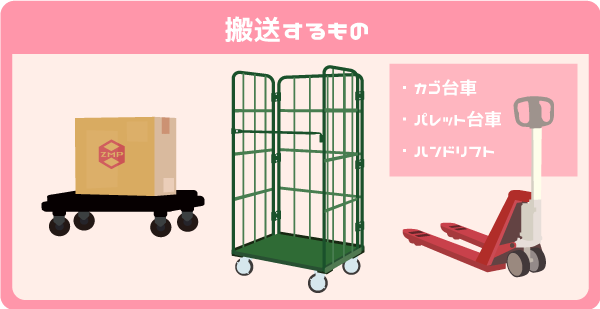
3. Low floor type
Low floor AGVs that transport goods by moving under pallets and lifting them. Low floor AGV can be used to carry pallets and racks and unload them at vehicle destinations, allowing transport without human intervention. This reduces the waiting time of the AGV effectively.
Because it is a low floor AGV, it can carry pallets and wheelless carts. It is also useful when transporting cart without towing parts.

The AGVs themselves have been used in manufacturing plants since the 1980s. Up to now, many different methods of navigation have been developed. Although it is important to compare the cost of setting up the route and the accuracy of the vehicle, choosing an AGV with the right navigation method is even more important.
We will introduce some typical methods of navigation below:
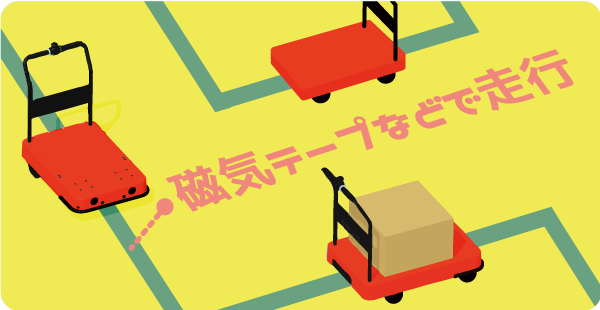
1.Magnetic line navigation
Magnetic line navigation is a method of determining the path of an AGV vehicle mainly by applying magnetic tape on the floor. Thanks to the magnetic sensor mounted on the vehicle, it can accurately read the path with stop accuracy and the straight line. In addition, when compared to the underground wire guiding type, this method is more widely used, because it is less costly to install. In addition to navigation by magnetic lines, people also use other navigation methods such as: reflective tape, electromagnetic induction cable.
2.SLAM Navigation
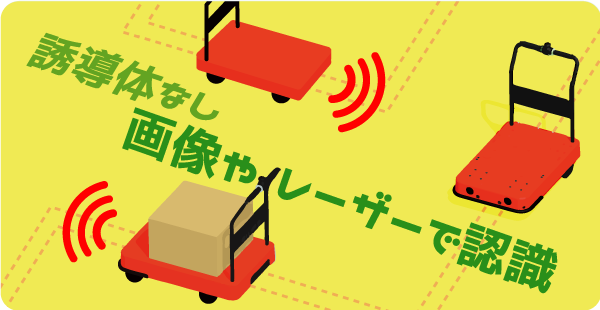
SLAM stands for “Simultaneous Localization and Mapping”, which means to determine the position and at the same time create a path drawing, which is a guiding method where the robot can both accurately grasp its position and move, without having to equip anything on the floor, the robot’s path. It is exactly called AMR but many people still call it AGV.
The method of determining the position of the robot is based on “LiDAR SLAM” that can measure the distance from it to surrounding objects thanks to the laser reflected from the object about it, and “Visual SLAM” by determining high-level visual perception technology.
The SLAM navigation method is applied a lot when the factory cannot fix the magnetic line and the position of the shelves and carts has to be changed frequently. In addition, in environments where many forklifts are used, the magnetic lines glued to the floor will easily peel off, so the AMR type of navigation will come into play.
Recently, when choosing an AGV, in addition to “Navigation method “, “Transport mode“, people are increasingly attaching importance to “Link function“.
If you consider the factories, although it is possible to automate the transportation process, tasks such as loading goods up, placing orders down, inspecting goods still need to be manipulated by humans. The true meaning of automation, reducing labor is that AGV can relate different jobs around the transportation stage.
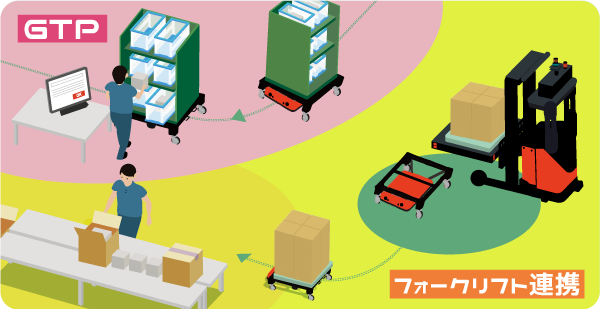
Link with forklift, pick up goods
Depending on the type of AGV, before automatic transportation, it is necessary to do the work of placing the product on the cart or rack. Loading work can be done unmanned and efficiently.
AGV and loading work are linked together, you can think of linking an unmanned forklift in a warehouse with an automatic palletizing machine in a product production line. Besides. there is also a method of linking from the stage of transporting goods to the area where the workers load the goods (GTP – Goods to person).
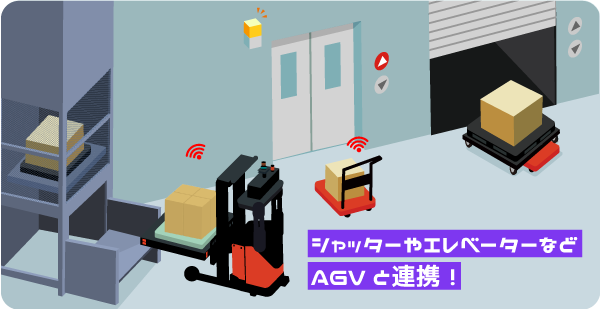
Linking rolling doors and elevators
In human-made transportation, AGV will encounter difficulties on the way such as rolling doors, security doors, and elevators. If these devices are linked to AGVs, things that used to be done only by humans can now be fully automated.
Link bus system
Loading and unloading at the terminals, where trucks come and go, are typical locations involved in transportation. By linking the incoming/outgoing truck management system with the AGV, the AGV will arrive at the right time when the job is required, enabling efficient transportation.

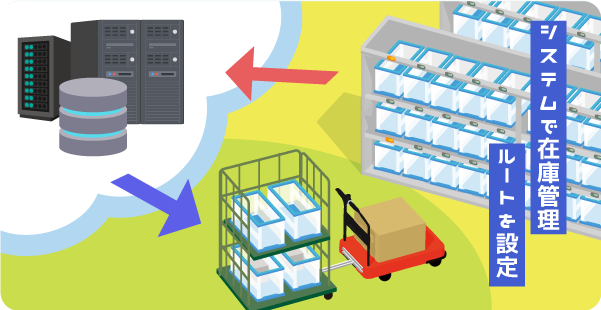
Integration with warehouse management system (WMS)
In the warehouse, where are the goods and what are the goods? It is very necessary to set up the path of the AGV. By linking the AGV with the WMS (warehouse management system) that manages inventory and ships/receives information as data, it is possible to set up a route according to the situation.
Advantages of putting AGV into practice:
Cost reduction, high efficiency
Thanks to the adoption of AGV, how much costs can be reduced becomes extremely important. As for the cost that can be cut, it is not only possible to reduce the labor force, but also reduce the cost of defective goods due to the carelessness of workers when they have to work hard.
You should consider looking at hidden costs after installation, such as whether it will update or whether the AGV can be linked to other devices and services.
If you can only buy a few AGVs and the system that comes with them, the cost of AGVs can double. There are a few vendors that can let you test 1 AGV, if so try to calculate the cost.
Outstanding functionality and low-cost will mean nothing if the AGV is not right for your factory.
Choose the most suitable AGV for your factory by knowing the characteristics of the warehouse or factory, such as transport areas, areas of robots and people, and externally linked equipment can increase efficiency after putting AGV into practice.
The first thing to do is to discuss with manufacturers to understand the requirements.
In fact, it is very difficult to choose which type of AGV, which function to choose.
If you consult with us, we can recommend a labor-saving or automation solution that works best for you.
If you are considering using AGV, contact us now !
